Calcium is not just about strong bones; it plays a crucial role in various bodily functions, from muscle contractions to nerve signalling. When your body lacks sufficient calcium, it can lead to a range of symptoms that shouldn't be overlooked. Here are ten signs that might indicate you're not getting enough calcium:
1. Brittle Nails
If you find your nails breaking easily or becoming brittle, it could be a sign of calcium deficiency. Calcium contributes to nail strength, and when levels are low, nails may become fragile and prone to splitting.
 Photo by Ellie Eshaghi on Unsplash
Photo by Ellie Eshaghi on Unsplash
2. Muscle Cramps
Are you experiencing unexplained muscle cramps, particularly in the legs or arms? Low calcium levels can disrupt muscle contractions, leading to painful cramps even with minimal exertion.
 Image by Milius007 from Pixabay
Image by Milius007 from Pixabay
3. Dental Issues
Calcium is vital for maintaining healthy teeth and gums. If you're experiencing frequent cavities, tooth decay, or receding gums, it could be a sign of insufficient calcium intake.
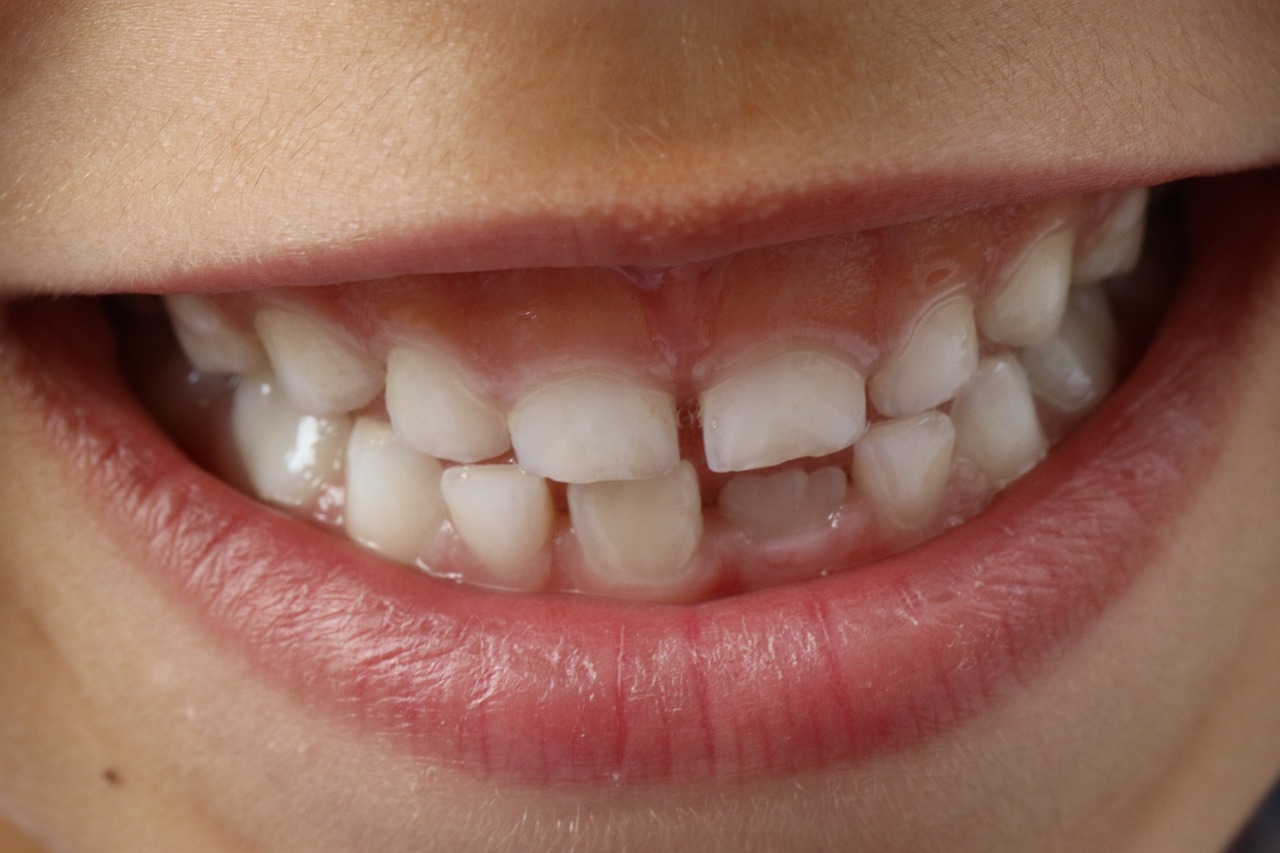 Image by Josef Pichler from Pixabay
Image by Josef Pichler from Pixabay
4. Numbness and Tingling
Tingling sensations or numbness in the extremities, such as the fingers, toes, or lips, may indicate nerve damage due to low calcium levels. Calcium is essential for nerve function, and deficiency can lead to these uncomfortable sensations.
 Image by Sookyung An from Pixabay
Image by Sookyung An from Pixabay
5. Osteoporosis Risk
One of the most well-known consequences of chronic calcium deficiency is an increased risk of osteoporosis. Without enough calcium, bones can become weak and porous, making them more prone to fractures.
 Image by Dr. Manuel González Reyes from Pixabay
Image by Dr. Manuel González Reyes from Pixabay
6. Fatigue
Feeling unusually tired or fatigued, even after getting enough rest, could be a sign of calcium deficiency. Calcium plays a role in energy metabolism, and inadequate levels can leave you feeling drained and lethargic.
 Image by LATUPEIRISSA from Pixabay
Image by LATUPEIRISSA from Pixabay
7. Poor Bone Density
Low bone density, often detected through a bone density scan, can indicate calcium deficiency. Without sufficient calcium, your body may not build and maintain bone mass effectively, leading to weaker bones over time.
8. High Blood Pressure
While many factors contribute to high blood pressure, inadequate calcium intake can play a role. Calcium helps regulate blood pressure by assisting in smooth muscle contraction within blood vessels. Insufficient levels may contribute to hypertension.
 Image by Gerald Oswald from Pixabay
Image by Gerald Oswald from Pixabay
9. Irregular Heartbeat
Calcium is crucial for the proper functioning of the heart, including regulating heartbeat rhythms. A deficiency in calcium may lead to irregular heartbeats or palpitations, which should be evaluated by a healthcare professional.
 Image by Stefan Schweihofer from Pixabay
Image by Stefan Schweihofer from Pixabay
10. Difficulty Losing Weight
Despite efforts to maintain a healthy diet and exercise routine, if you're struggling to lose weight, calcium deficiency could be a contributing factor. Some research suggests that calcium may play a role in regulating fat metabolism, and insufficient levels could hinder weight loss efforts.
 Image by Vidmir Raic from Pixabay
Image by Vidmir Raic from Pixabay
Preventing calcium deficiency is essential for maintaining optimal health and avoiding a range of associated symptoms. Fortunately, there are several simple strategies you can incorporate into your lifestyle to ensure you're getting enough calcium. Here are ten effective ways to prevent calcium deficiency:
1. Consume Calcium-Rich Foods
Incorporate a variety of calcium-rich foods into your diet, such as dairy products like milk, cheese, and yogurt, as well as leafy green vegetables like kale and broccoli. Other sources include fortified foods like tofu, orange juice, and cereals.
 Image by Myriams-Fotos from Pixabay
Image by Myriams-Fotos from Pixabay
2. Get Plenty of Vitamin D
Vitamin D is crucial for calcium absorption in the body. Ensure you're getting enough sunlight exposure, consume vitamin D-rich foods like fatty fish, eggs, and fortified dairy products, or consider taking a vitamin D supplement if needed.
 Image by 💌🌸🌷Marion 🌷🌸💌 Wellmann from Pixabay
Image by 💌🌸🌷Marion 🌷🌸💌 Wellmann from Pixabay
3. Limit Caffeine and Soda
High intake of caffeine and soda can interfere with calcium absorption and increase calcium excretion through urine. Limit your consumption of these beverages to help maintain calcium balance in your body.
 Image by 13758299 from Pixabay
Image by 13758299 from Pixabay
4. Quit Smoking
Smoking has been linked to decreased bone density and increased risk of fractures. Quitting smoking can help protect your bones and prevent calcium loss, contributing to overall bone health.
 Image by Gerd Altmann from Pixabay
Image by Gerd Altmann from Pixabay
5. Engage in Weight-Bearing Exercise
Regular weight-bearing exercises, such as walking, jogging, dancing, or weightlifting, help stimulate bone growth and maintenance. Aim for at least 30 minutes of weight-bearing exercise most days of the week.
 Image by alba1970 from Pixabay
Image by alba1970 from Pixabay
6. Avoid Excessive Alcohol Consumption
Heavy alcohol consumption can interfere with calcium absorption and affect bone health. Limit alcohol intake to moderate levels or avoid it altogether to prevent calcium deficiency and related complications.
 Image by Michal Jarmoluk from Pixabay
Image by Michal Jarmoluk from Pixabay
7. Consider Calcium Supplements
If you're unable to meet your calcium needs through diet alone, consider taking calcium supplements under the guidance of a healthcare professional. Choose supplements that contain calcium citrate or calcium carbonate for better absorption.
 Image by HeungSoon from Pixabay
Image by HeungSoon from Pixabay
8. Maintain a Healthy Weight
Being underweight or overweight can negatively impact bone health and increase the risk of calcium deficiency. Aim for a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise to support optimal bone density.
 Image by Vidmir Raic from Pixabay
Image by Vidmir Raic from Pixabay
9. Prioritize Calcium During Pregnancy and Breastfeeding
Pregnancy and breastfeeding increase calcium requirements to support both maternal and fetal bone health. Ensure you're consuming adequate calcium-rich foods or supplements during these life stages.
 Image by Robster_91 from Pixabay
Image by Robster_91 from Pixabay
10. Regular Health Checkups
Regular health checkups can help identify any potential risk factors for calcium deficiency or related conditions. Consult with your healthcare provider for personalized recommendations based on your age, gender, medical history, and lifestyle factors.
 Image by Darko Stojanovic from Pixabay
Image by Darko Stojanovic from Pixabay
KEEP ON READING

20 Food-Related Art Projects