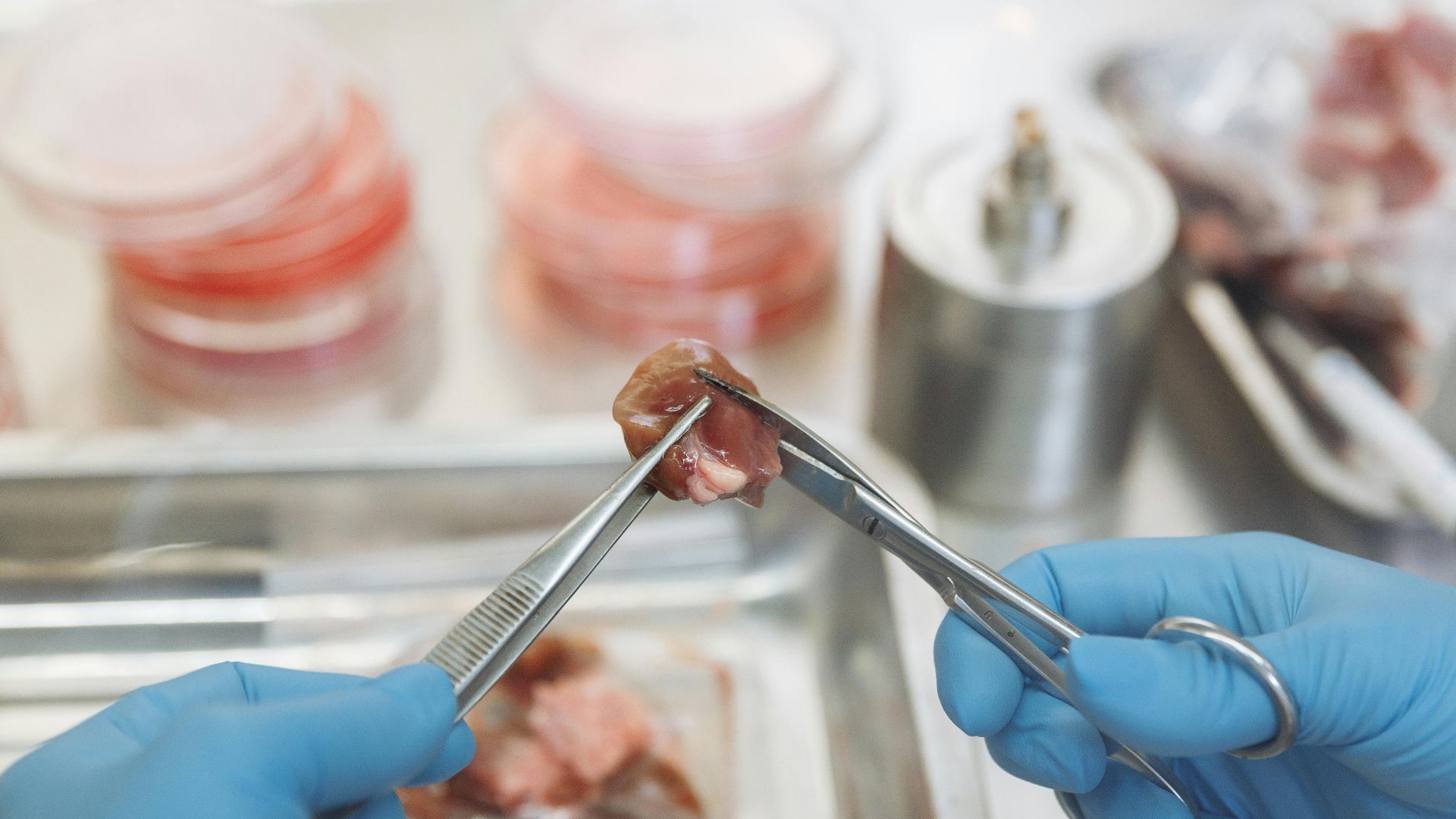
Cultivated Meat: What You Need to Know Before Taking a Bite
Lab-grown, cultivated, cultured, clean—no matter what you call it, this isn't your regular cut of meat. Instead, it's protein made from animal stem cells, placed in large steel tanks called bioreactors, then fed nutrients to form the basic components of meat. While the science behind it is commendable, as are its benefits—the biggest one being improved animal welfare without the need for slaughter—you might still pause before you take a bite. Is this advancement as great as it claims to be? Here are 10 drawbacks you should know about and 10 potential benefits.
1. High Costs
One of the biggest disadvantages of cultivated meat is its high cost. While there have been improvements on this end—the first clean-meat burger made from thin strands of muscle tissue cost over $300,000 to produce in 2013, compared to today's cost of $500 for a quarter pound—it's still unlikely that people would shell out that much money.
2. Limitations of Biological Cell Growth
Another limitation that innovation may never be able to change is biological cell growth. Scientists have tried to experiment and test the question: Is it possible to pack as many cells as possible in a bioreactor (a steel tank where the cells are grown) without the cells dying in the process? The answer, it seems, is no, which means growing meat won't ever be cost-effective.
3. Scaling Challenges
In order for lab-grown meat to become widely available, production levels would need to meet global demand—something that doesn't yet seem possible. For one, there are the limits of biological cell growth. Scientists also have to figure out different ways to make cells grow faster and how to pack more into the same space.
4. Ethical Concerns
While one of the main pluses of cultivated meat is that it's slaughter-free—improving animal livelihood—the process still raises ethical questions and concerns. The reason being is that the animals still need to be sedated and anesthetized to perform biopsies, so that these stem cells can be grown.
5. Unknown Health Risks
Those who may have cut out meat from their diets due to health concerns, such as high cholesterol, might be willing to try cultivated meat, due to the ability for scientists to swap out saturated fat for healthier fats like omega-3 fatty acids. However, because lab-grown meat goes through high-level cell multiplication—much in the same way cancer cells mutate and multiply—there could be abnormalities that pose health risks in the long run.
6. Energy-Intensive Production
Cultivated meat can be an energy-intensive process, despite arguments saying that it releases less greenhouse gases than traditional farming. But where those sources focus on the use of water and land, they don't take into account the bioreactors needed to house the cells, which may produce even double the carbon emissions than that of raising livestock.
7. Labeling Issues
In 2019, the United States Department of Agriculture and Food and Drug Administration issued it mandatory for all cultivated meat packages to be labeled accordingly and transparently when being sold. But some organizations, like Good Food Institute, disagreed with this, stating that label censorship is unconstitutional and undermines the free market.
8. Textures & Flavors Can Differ
If cultivated meat is to replace regular meat, then we should hope its taste and texture match the original, right? While many agree that lab-grown meat isn't too far off in terms of replicating flavor, it's the texture that can sometimes be different. For example, some note that cultured chicken tastes richer and chewy, while cultured beef tastes softer and looser than the real thing.
9. Limited Availability
Lab-grown meat isn't yet widely made available, and it's unlikely you'll find it in your closest supermarket any time soon. Those impatient and eager to try aren't without a solution; you can fly out to Singapore for a taste of science in selected restaurants.
10. It's Still Meat
No matter how you slice it, at the end of the day cultivated meat is still meat. Vegetarians and vegans are unlikely to be convinced in trying it, since cell samples are still taken from animals, which are then grown in lab tanks. As for the curious, though, that's a whole different story.
But in saying all that, what about the benefits? Let's jump into that next.
1. Reduced Environmental Impact
Traditional agriculture requires a lot of land and water, two things that lab-grown meat doesn't rely on as much. On top of that, cultivated meat produces significantly less carbon emissions than livestock farming. According to a 2022 report published by the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, it's estimated that livestock accounts for 11.1-19.6% of global greenhouse gases.
2. Better Animal Welfare
The obvious positive of cultivated meat is that it improves the livelihood of the animals. While biopsies will still need to be performed on them, there's no more need for raising and slaughtering cruelty in traditional livestock farming, where contaminated environments also cause stress and pose health issues for the animals.
3. Lower Risk of Contamination
Expanding on the previous point, because cultivated meat is grown in a sterile, controlled environment, there's less possibility for contamination and foodborne illnesses. And that advantage is passed on to you, the person consuming the meat. In traditional farming, animals are often fed antibiotics to prevent disease—but there's no need for this if they're raised in optimal environments.
4. Less Saturated Fat
Another advantage of lab-grown meat is the ability for scientists to control exactly how much saturated fat the end product has—or none at all. It can even be replaced with healthier fats that are good for us. And since red meat being high in saturated fat is the reason why most stray away from it, this is a major plus point.
5. Improves Food Security
While scientists still need to figure out how to maximize scaling levels to meet global demand, once cultivated meat becomes widely available, it can become a reliable source of protein. We would no longer need to worry about outside factors that may inhibit production, like weather, seasonal changes, environmental concerns, and health issues.
6. Customizable Options
Along with adjusting saturated fat levels, lab-grown meat can also be customized in other ways. If you want to change the protein-to-fat ratio, want a specific cut, or prefer certain textures and flavors, these variations can be arranged. Almost like it's made to order.
7. Antibiotic-Free
As mentioned previously, because lab-grown meat is raised in a sterile environment, there's no risk of unknown additives or antibiotics being present in the end product. Whereas with traditional farming, animals are often raised in crowded, unsanitary spaces, and are then fed antibiotics to prevent disease.
8. Hormone-Free
On top of being antibiotic-free, cultivated meat is also free from synthetic hormones like estrogen and testosterone which are fed to animals (such as in the United States and Canada) to make them grow larger and faster. These added artificial hormones may increase the risk of disease and cancer when consumed, making cultivated meat a healthier option on this end.
9. Reduce Global Hunger
If lab-grown meat becomes a reliable and sustainable source of protein, it could not only address food shortages but may even reduce global hunger. This is a big positive, considering estimations that the world population could increase to 9.2 billion by 2040, and over 10 billion by 2050.
 tortugamediaservices on Pixabay
tortugamediaservices on Pixabay
10. Scientific Advancements & Discoveries
With cultivated meat on the rise, it's encouraged and strengthened development in other areas, pushing the boundaries of what's possible and attainable. Further experiments and research have allowed scientists to explore tissue regenerative medicine and advanced bioreactor technology (which allow for large-scale production), among others.
KEEP ON READING