10 Reasons Why Meat is Bad for You & 10 Reasons Why It's an Essential Part of Our Diets
10 Reasons Why Meat is Bad for You & 10 Reasons Why It's an Essential Part of Our Diets
Is It Time to Give Up Bacon?
Is meat good for you or not? Scientists and health experts have long studied the pros and cons of eating meat, particularly red meat. While it's generally agreed that red and processed meats, such as bacon, aren't the healthiest choices, there's no definitive answer on whether we should cut this source of protein from our diets entirely. What's your take on the debate? Let's take a look at 10 reasons why meat may be bad for you—and 10 reasons why it should be an essential part of your diet.
1. High in Saturated Fat
Red meat—think beef, pork, lamb, mutton, and veal—is high in saturated fat, which becomes solid at room temperature. This is also the kind of fat that increases LDL or bad cholesterol, and the more saturated fat we eat, the higher our risk of cardiovascular disease, type 2 diabetes, stroke, and other health issues.
2. Hardens Blood Vessels
It's not just saturated fat that can build up your arteries, either. Research has found that a particular compound in meat, carnitine, can cause hardening of the vessels the same way fats can clog these vital pathways. Upon digestion, carnitine is then converted into a damaging compound called trimethylamine-N-oxide (TMAO) by gut bacteria, which can significantly increase the risk of heart disease.
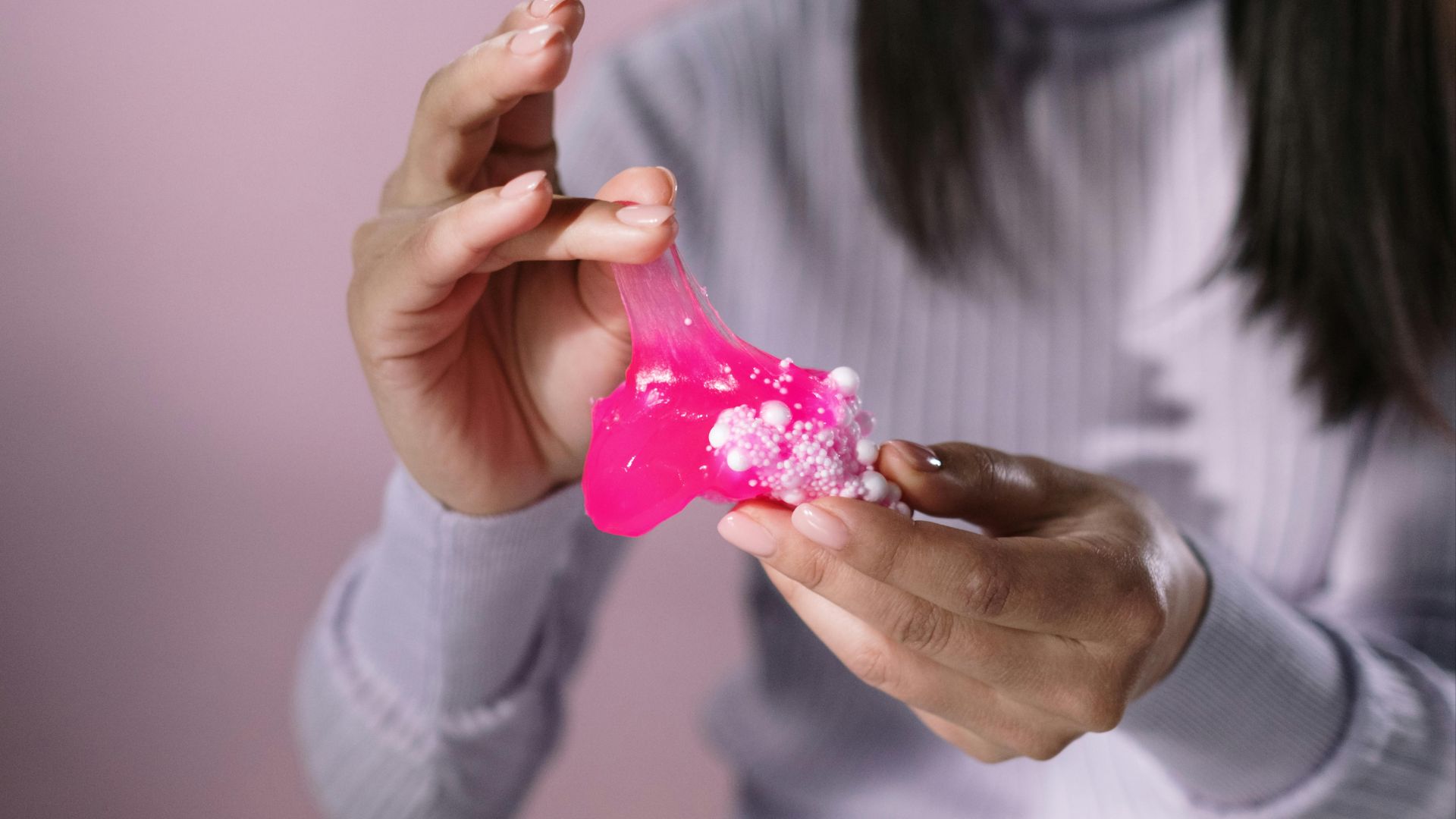
3. You're Eating Pink Slime
You may have heard of this before, that the meat you're consuming from fast food chains isn't completely meat. Instead, you could be eating pink slime (scientifically known as lean finely textured beef, or LFTB)—a filler made from meat trimmings that are spun to remove fat, then treated with ammonia to kill harmful bacteria. While it's technically safe to consume, it's essentially processed goop.
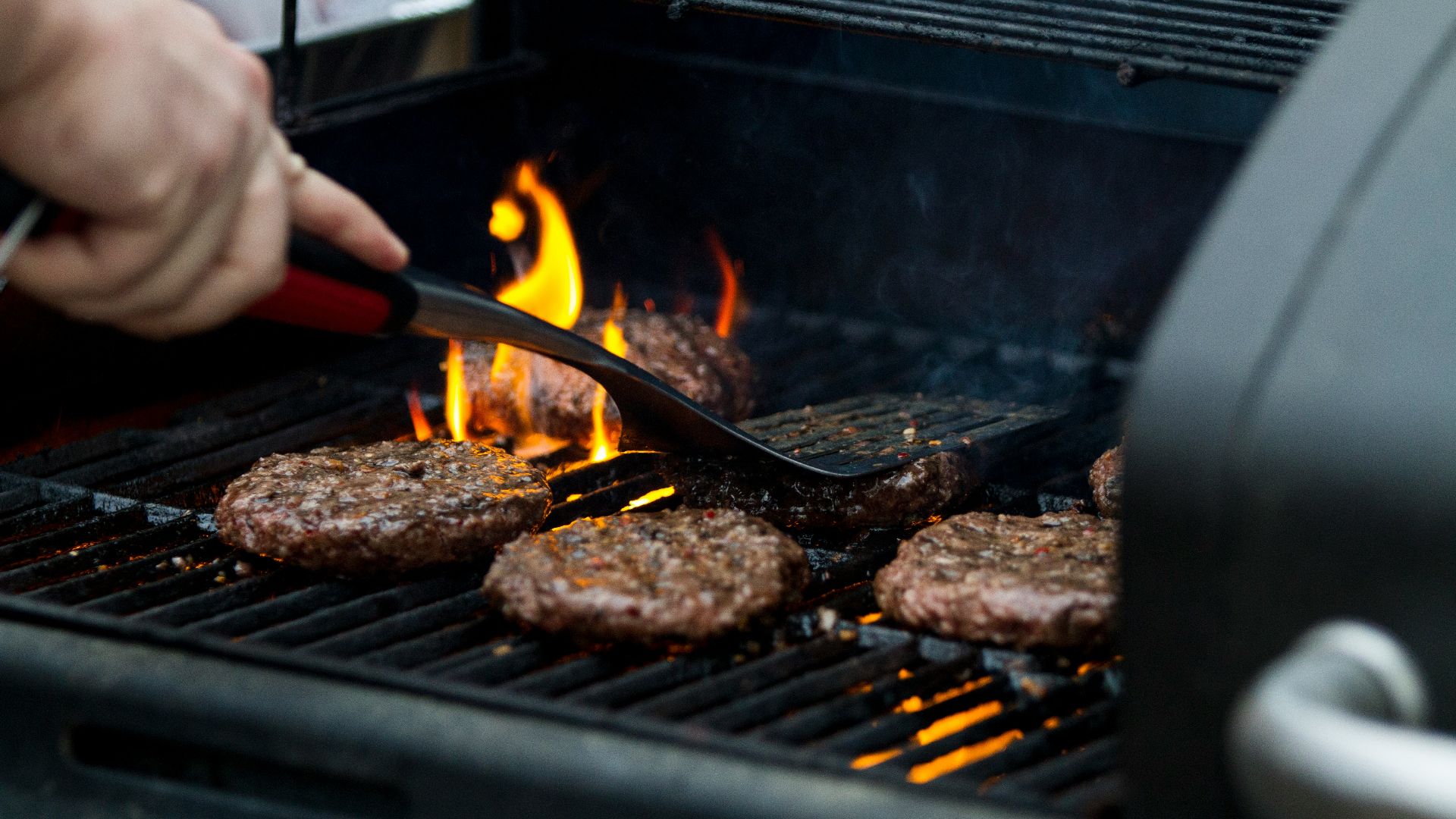
4. Cooking Creates HCAs and PAHs
The way you cook meat also matters. At high temperatures—over 300°F, for example—compounds called heterocyclic amines (HCAs) and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) are formed. These two substances, according to research, may alter DNA. This means frequently consuming barbecued meats, grilled steaks, or other high-temperature-cooked proteins may increase your risk of cancer.
5. You Could Get E. Coli
E. coli can be contracted through consuming raw or unpasteurized milk, apple cider, or contaminated food and liquids. But how does that come into play with cooked meat? Depending on how many animals went into producing your burger patty—as few as 10 or as many as 1,000—you could potentially become sick with E. coli if any part of that meat was infected during processing.
6. Raising Livestock Harms the Environment—& Them
Raising livestock takes a severe toll on the environment. For one, traditional agriculture requires vast amounts of land and water, and livestock farming significantly contributes to the emission of greenhouse gases, accounting for nearly 15% of the global total. And that's not all—it's especially awful for the animals, too, who suffer through extreme cruelty just to get that cut of steak on your plate.
7. Could Contain Antibiotics & Added Hormones
Livestock farming isn't grand. Many animals are fed poor diets and injected with antibiotics to treat, control, and prevent disease. They're also given growth hormones so that they mature faster and stronger. For us, that means those added drugs are passed onto our bodies when we consume meat. Research suggests that eating too much hormone-riddled red meat can increase the risk of breast cancer in women.
 Raghavendra V. Konkathi on Unsplash
Raghavendra V. Konkathi on Unsplash
8. Increased Risk of Heart Disease & Type 2 Diabetes
Because meat contains high amounts of saturated fat, eating too much over time can raise the risk of developing chronic health conditions, like type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease. As more plaque builds up in the arteries and blood vessels, you could experience something even more fatal, such as a heart attack or stroke.
9. Increased Risk of Obesity
Saturated fat also puts you at risk of weight gain, as does consuming too much processed meat, such as bacon, ham, salami, jerky, sausage, and other smoked meats. This is due to not only the unhealthy excess content in the protein, but also because of its high caloric profile. In fact, those who eat meat are far more likely to become overweight than those who don't.
10. Increase Risk of Cancer
Perhaps the most discussed concern is the negative impact meat can have on the body and how it may put us at risk of developing cancer. Red meat and processed meat contain, as mentioned, high amounts of saturated fat as well as added preservatives that go into curing or salting them. This greatly raises the chance of liver disease, stomach cancer, and colorectal cancer, among others.
Does this mean you should drop meat altogether? Before you make a decision, it's important to note that meat isn't always bad—it just depends on what type and how much of it you eat. Let's take a look at 10 reasons why it should be an essential part of your diet.
 Michelle @Shelly Captures It on Unsplash
Michelle @Shelly Captures It on Unsplash
1. Great Source of Protein
Meat is one of the greatest sources of protein. Three ounces of lean beef amounts to nearly 25 g of protein. In contrast, eggs contain around 6-8 g of protein, meaning you would have to eat at least three of them to get the same amount.
2. Contains Essential Nutrients
Not only is meat packed with protein, it also contains numerous essential nutrients, such as zinc, iron, and selenium. These minerals help fortify the immune system, transport oxygen, form healthy red blood cells, and help protect your cells from damage. In particular for iron, meat is abundant in heme iron which is easily digested by our bodies, as opposed to non-heme iron found in plant-based diets.
3. Contains Important Vitamins
Meat is also loaded with important vitamins, such as calcium, and vitamins A, B12, and D—all of which are essential for our bodies to function the way they should. In fact, animal-derived foods like meat are one of the greatest—and possibly only—dietary sources of vitamin B12, which is key for blood cell formation and ensures proper development and maintenance of the brain and nervous system.
4. Supports & Strengthens Bone Health
As you age, your bones become weaker and more brittle. It's a good thing meat is made up of a crucial component that ensures your bone health stays in tip-top shape—protein. But be careful: too much of anything can be a bad thing, and some researchers believe that too much protein can also lead to osteoporosis.
5. Can Boost Brain Function
Protein and other nutrients and amino acids, such as vitamin B12, iron, and omega-3 fatty acids, present in meat also support brain health. These essential components help to increase concentration by boosting mood and energy levels.
6. May Help Mental Health
Research suggests that eating meat can also support certain mental health conditions, such as depression and anxiety. For one, meat contains various nutrients—think tryptophan and vitamin D—that are required to make serotonin, a feel-good hormone that affects mood, learning, memory and fear. While this doesn't mean you should regard this as a magic cure, this may be reason enough to add meat to your diet.
7. Promotes Muscle Growth
If you're looking to grow your muscle mass, you may already know the importance of consuming more protein. And apart from protein bars and shakes, where else can you get a good source of this macronutrient? Meat. Research has shown that consuming meat post-workout helps facilitate not only muscle growth but also repair tissue damage.
8. Increases Satiety & Reduces Cravings
You might have heard that eating foods that are high in protein keeps you full. And it's true—protein is far more satiating than other nutrients, like carbohydrates or fat, simply because it takes longer for the body to digest and break down. In turn, that also means you won't be as likely to reach for snacks to curb cravings afterwards because you're still full.
9. Promotes Healthy Hair, Skin, & Nails
Nutrients like protein, iron, zinc, and B complex vitamins like thiamin, niacin, riboflavin, vitamin B6, and vitamin B12 in meat also support healthy hair, skin, and nails. That means if you struggle with brittle nails or chronic skin conditions such as eczema or psoriasis, incorporating more protein in your diet may help alleviate the problem.
10. May Help Boost Immune System
The nutrients in meat also help strengthen and support the immune system. B complex vitamins and zinc, for example, aid in the development of white blood cells, T cells, wound healing, cell regeneration, and more. So, if you find your immunity isn't the best, it might mean you need to add more meat to your meals.
KEEP ON READING

20 Food-Related Art Projects

























